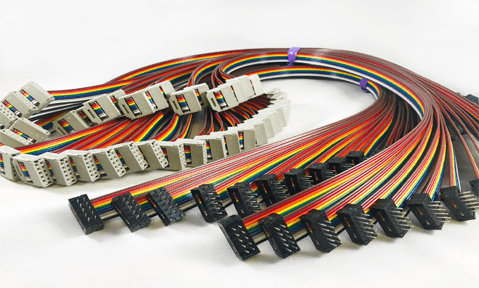
A broad, flat strip of insulating material is connected to numerous conducting wires that are arranged parallel to one another to form ribbon cables. Because of their small size, flexibility, and well-organized design, these cables—hence their name—are frequently found in computers, electronics, and communication devices.
This article explores the types, applications, benefits, and structure of ribbon cables as well as their significance in the current electronics industry.
1. Ribbon cable components and structure
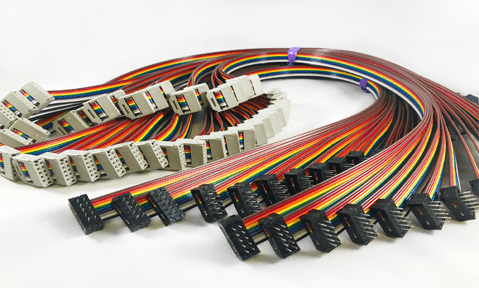
Ribbon cables are often composed of several insulated wires placed side by side and are intended to be thin, flat, and flexible. The material typically used to make these cables is copper, which has a high conductivity. To guard against electrical shorts and environmental damage, a layer of plastic insulation—typically polyvinyl chloride (PVC)—is placed over the wires.
a. Principal Elements:
Ribbon cables have a flat and flexible design that makes it simple to route them through small places, which makes them perfect for use in small electrical equipment.
many Conductors:
Ribbon cables are appropriate for applications that call for the simultaneous transmission of many signals since they have numerous conductors arranged in a parallel fashion.
Standard Color Coding:
Ribbon cables frequently have color-coded insulation for each conductor to make it easier to identify individual wires. Because of the defined procedures this color coding adheres to, installation and troubleshooting are made easier.
b. Ribbon cable types:
Based on the quantity of conductors, dimensions, and intended applications, ribbon cables are available in a variety of configurations. Several typical varieties consist of
Standard ribbon cables are flexible, flat wires that are utilized in a wide range of electronic applications.
Ribbon cables with twisted pairs of conductors are known as twisted pair ribbon cables, and they are designed to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) in delicate applications.
Shielded Ribbon Cables: Shielded ribbon cables offer defense against outside electrical noise in high-EMI settings.
Some ribbon cables are made with a rounded cross-section to accommodate particular equipment or devices in spaces that are limited in size.
2. Ribbon Cable Applications
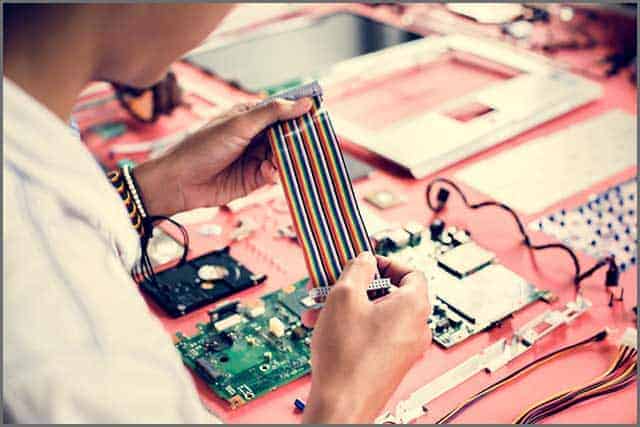
Ribbon cables are used in many different industries, particularly in the fields of electronics, computing, and communication systems. They are the perfect option for joining internal components in devices with limited space because of their tiny and flexible design.
Electronics and Computers
In computers and other electrical devices, ribbon cables are used extensively. They are frequently used to link internal parts including motherboards, optical drives, and hard drives. Ribbon cables were commonly used in the early days of personal computers to connect CD-ROM drives and hard drives to the motherboard via IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) connections.
Ribbon cables are still used in many forms in modern computers, especially when connecting older hardware and in scenarios where a thin, low-profile cable is required.
a) Scanners and printers
Ribbon cables are frequently used in printers and scanners to link moving elements to the main control board. For instance, a flexible ribbon cable connects the print head of an inkjet printer to the control electronics, enabling the head to move back and forth while retaining a stable electrical connection.
d. Equipment for Communication
Additionally, ribbon cables are frequently seen in networking devices, modems, and telecom systems. Ribbon cables offer a small and tidy solution to manage these connections. These devices frequently need to send several signals across short distances within the equipment.
d. Appliances for the Home
Ribbon cables are used by many home appliances, including microwaves, washing machines, and televisions, to link internal circuit boards, sensors, and control panels. Ribbon cables are flat and flexible, which makes it simple to route them through the tight places found in these equipment.
e. The aerospace and automotive industries
Ribbon cables are utilized in the internal electronics of automobiles and aircraft in the automotive and aerospace industries. They are used to link control panels, sensors,
3. Ribbon cables’ advantages
Ribbon cables are widely used in many different industries because they provide a number of benefits over other kinds of cables. Among these advantages are:
a. Effectiveness of Space
Ribbon cables are perfect for use in devices with limited space since they are flat and thin. They can be easily routed through small places, like those in closely packed machinery or small electronic devices, thanks to their compact shape.
c. Adaptability
Because of their extreme flexibility, ribbon cables can be used in situations requiring bending or movement. For instance, ribbon cables can flex and bend in printers, scanners, and robotics applications without causing damage to the wires or breaking the electrical connection.
c. Well-Ordered Wiring
Ribbon cables are kept tidy and orderly by having their wires arranged in parallel. This company
d. Transmission of Multiple Signals
Because ribbon cables have numerous conductors, they can transfer various signals at once. Because of this, they are perfect for applications like industrial control systems, computers, and communication devices that need to transmit data simultaneously.
e. Diminished Interference from Electromagnetics
A lot of ribbon cables are made with reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) in mind. Ribbon cables that are shielded or twisted pair are especially good at mitigating the effects of electromagnetic interference (EMI), which makes them appropriate for usage in high-electric noise conditions.
4. Difficulties and Restrictions

Ribbon cables have numerous benefits, but they also have certain drawbacks and difficulties that must be taken into consideration in particular situations.
1. Sturdiness
Despite being flexible, ribbon cables are more prone to breaking than other kinds of cables, especially if they are bent too sharply or experience a lot of wear and tear. Because of this, they are less appropriate for settings where the cable might be subjected to adverse weather or physical stress.
b. Limited Length
Since ribbon cables’ architecture is not ideal for long-distance transmission, they are typically utilized for short-distance connections within devices. Signal deterioration can happen over greater distances, therefore coaxial or fiber optic cables are better options.
d. Stress from Mechanical Action
The level layout of Ribbon cables are more prone to mechanical stress, particularly in situations where they must be bent or moved about a lot. The conductors inside a ribbon cable may break if it is bent at a steep angle over time, which could result in intermittent connectivity or signal loss.
d. Restrictions on Connection
Ribbon cables are generally used for internal connections within electronics; if not properly protected, they are not recommended for use in harsh exterior conditions. Ribbon cables need extra shielding or protective housings in outdoor or industrial environments in order to guarantee their dependability.
5. Conclusion: Ribbon Cables’ Significance in Contemporary Technology
Ribbon cables can appear to be a straightforward part, but they are vital for connecting and powering a lot of the everyday electronics we use. Ribbon cables are an effective and dependable way to transfer various signals in a small and well-organized package, and they may be found in everything from computers and home appliances to communication equipment and automobile systems.
Their adaptability, spatial economy, and capacity for multi-signal transmission render them an indispensable component of the contemporary electronics environment. Ribbon cables continue to be an essential part of many different industries despite certain limits with regard to long-distance transmission and durability. This is because of their high degree of adaptability and efficiency.
Ribbon cables may perform even better in the future because to new materials and designs that take advantage of technological advancements. Ribbon cables continue to be a necessary component of modern life, silently powering the gadgets and systems that keep our world connected, whether they are found in the internal workings of your laptop, the control systems of your car, or the electronic components of your home.